Nov 16, 2022
What Is Heat Shrink Tubing?
Heat shrink tubing serves as an extra layer of protection for cables and wires. This plastic material is inserted around a wire or cable to protect products from external elements and day-to-day wear. As a flexible tubing solution, heat shrink tubes fit seamlessly and securely around connections and wiring, allowing them to work properly even when bent or twisted.
Contact Us About Heat Shrink Tubing
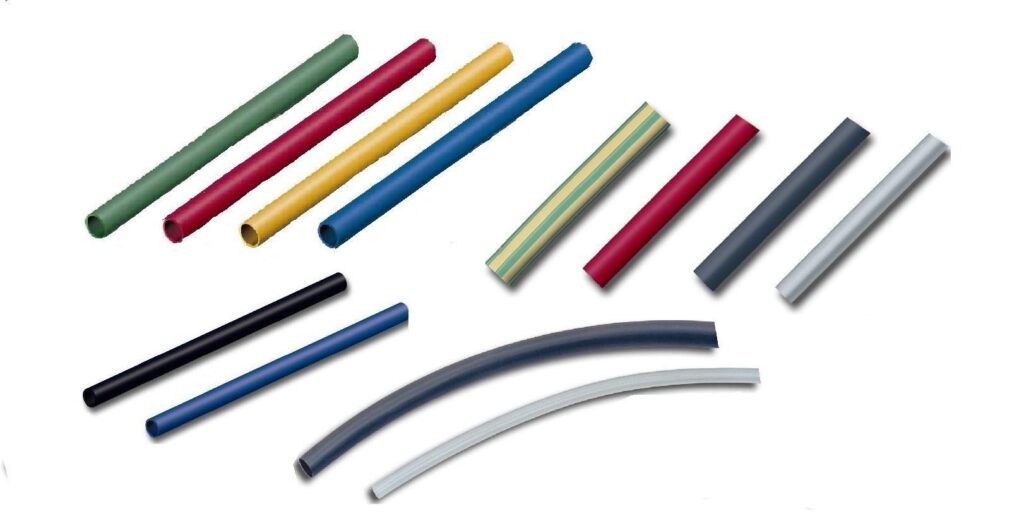
Different Types of Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing, usually made of polyolefin or nylon, shrinks whenever heated. After the heat shrink tubing cools off, it returns to its original relaxed state or diameter. There are many different types of shrink tubing, all designed for different purposes.
You can get tubing in flexible and adhesive options. You typically use flexible tubing on wires that need to bend, while adhesive-lined tubing has glue on the inner layer that melts as you apply heat to secure the connection once it dries. Here are some common types of shrink tubing:
- Fluoropolymer: Fluoropolymer tube or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a type of shrinkable tubing that has a considerable amount of resistance to punctures and harmful chemicals. It also has a very low friction coefficient and a wide range of operating temperatures.
- Viton: Viton is another type of shrink tubing that has a huge amount of chemical resistance. Often used in hydraulic equipment, it is very flexible and can operate at a very high temperature. These properties make Viton one of the most effective shrink tubing options whenever extreme temperature is a factor to consider.
- Elastomeric: Elastomeric shrink tubes can maintain very high flexibility even if they are subjected to very low temperatures. The tubes are highly resistant to chemicals such as petrol and diesel and can withstand the most severe environmental elements. They are also highly resistant to abrasion.
- Adhesive polyolefin: This type of shrink tubing is often used in the military, railway and aerospace industries. It is also widely manufactured because the material shrinks very fast and is highly flexible. However, it does have poor resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light — so low that only black polyolefin tubes are recommended for outdoor use.
- Silicone rubber: Silicone rubber tubing offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility. Fluorinated ethylene propylene, or FEP, is another type of shrink tubing that is considered a more affordable alternative to PTFE. Polyvinylidene fluoride is usually recommended for high-temperature usage.
Common Applications of Shrink Tubing
Due to its key properties and flexible capabilities, shrink tubes are widely used in various applications, including:
- Electrical insulation: Heat shrink tubing is a reliable insulation material for wires to facilitate safe operation.
- Component protection: Provide added protection for delicate components of key equipment and devices.
- Wire and cable bundling: Use shrink tubing as a protective sleeve to easily bundle wires and cables together.
- Color coding: Make accurate identification by using heat shrink tubing to color-code different wires and connections.
- Mechanical part cushion: Use heat shrink tubing around metal and other mechanical parts for precision and protection.
- Solder insulation: Create full insulation around soldered wirings for secure electrical projects.
- Impact resistance: Tubing products come with remarkable properties that withstand small impacts, strain and abrasion.
- Lightweight harnessing: If you need light harnessing for simple projects, you can count on shrink tubing for light, sturdy support.
How Polyolefin 2 to 1 Heat Shrink Tubing Works for Your Requirements
Designed to shrink to half its size with the application of heat, this product securely covers wires, joints, cables and terminals to ensure safe and effective electrical operations. By covering these high-usage areas, the tight, flexible shrink tubing offers superior protection against environmental elements that could impede functionality.
Typical applications for this product include:
- Component protection: Heat shrink tubing provides secure protection for delicate components that keep devices and equipment running.
- Wire bundling: With heat shrink tubing, you can easily bundle wires together in a protective sleeve.
- Insulation: Polyolefin heat shrink tubing can serve as insulation for wires to facilitate safe operation.
- Mechanical protection: Protect mechanical pieces of your equipment with heat shrink tubing that can mold precisely around the parts.
- Solder insulation: Ensure full insulation for soldered wire connections with heat shrink tubing.
- Color-coding: Make accurate identification easy by using heat shrink tubing to color-code different wires and connections.
- Lightweight harnessing: If you need lightweight harnessing for an application, you can use heat shrink tubing to provide the light, sturdy support your project requires.
- Strain relief: Provide a reliable transition from a flexible cable to a rigid connection point or wire with heat shrink tubing as a strain relief.
- Wire identification: To make specific parts stand out, identify critical wires for electrical repairs and maintenance with heat shrink tubing.
About Our Polyolefin Heat Shrink Tubes
At WesBell Electronics, we are committed to providing the highest quality heat shrink tubing for a wide range of applications. Our basic Polyolefin 2 to 1 heat shrink tubing can shrink to half its size with the application of heat to cover joints, wires, terminals and cables. Use shrink tubing to maintain safe and effective electrical operations. The polyolefin heat shrink tube also protects wires from environmental elements.
You can also get the same polyolefin heat shrink tubing in the 3:1 or even 4:1 shrink ratio. These larger ratios mean you can more easily slide them around larger components, such as wire harnesses. Many also come with adhesive glue on the inside, so you can permanently shrink the tubing onto the hook-up wire. If you use adhesive, it will be very difficult to remove the tubing, and if you can take it off, it will leave residue on the wire.
How to Use Shrink Tubing
Follow these easy steps to apply shrink tubing to your wires:
- Prepare the wire or cable and measure its diameter.
- Choose a heat shrink tubing big enough to slide into the connection.
- Insert the tubing into the wire.
- Shrink the heat shrink tubing using a heat gun.
- Make sure the tubing is tightly secured.
Be sure to keep the heat gun moving over the shrink tubing. Applying direct heat to one place can damage the wire.
Shop High-Quality Heat Shrink Tubing
WesBell Electronics is your trusted supplier for excellent heat shrink tubing. We also offer a wide range of wires, cables and other supplies for your electrical applications. Browse our affordable, high-quality products or get in touch with us today to reach one of our experts.







