Apr 20, 2021
TFFN vs. THHN Wire
Choosing wire for various projects requires understanding the specific ratings for different wire types. When it comes to wires with acronyms, knowing what makes each type distinct can be difficult. For instance, many people find they need help understanding the difference between TFFN and THHN wire because their names are so similar. Knowing the differences and the applications of these wires will make choosing the right one for your next project easier.
What Do the Wire Letters Stand for?
The letters used in wire names, such as THHN and TFFN, have specific representations to make identifying the uses of the cables easier. Break down the names by each letter code to understand what the cable names mean.
In both THHN and TFFN, the names start with T, which stands for thermoplastic, the type of insulation they share. Any other wire types that start with T also have thermoplastic insulation.
The N in both names refers to the type of material used for the exterior coating. In the cases of TFFN and THHN, that jacket has a nylon construction. This nylon exterior protects the wire from dust, dirt, gas and oil.
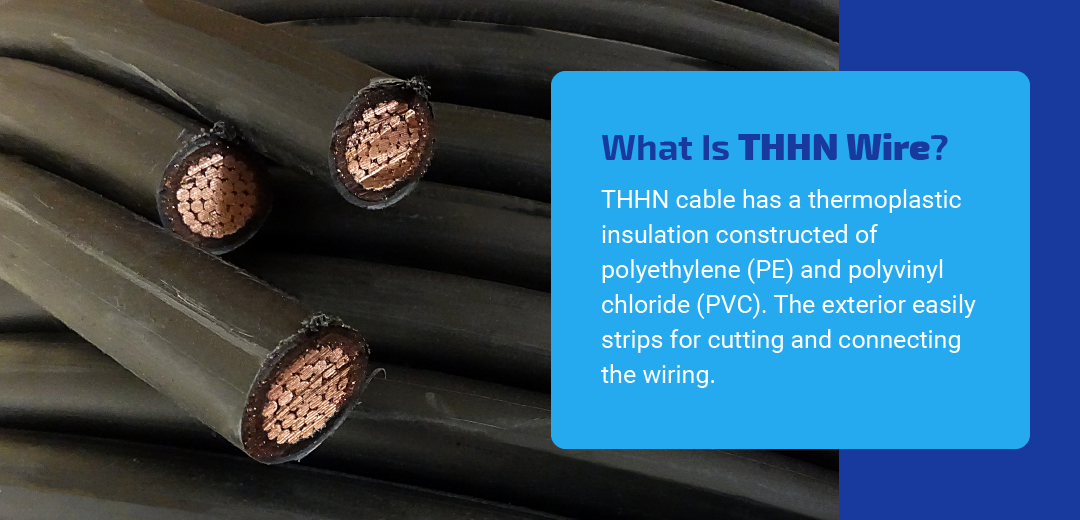
What Is THHN?
THHN wire means Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant Nylon-Coated. In THHN, each H represents a different level of heat tolerance for the wire. Names that only have one H can operate up to 75 degrees Celsius (167 degrees Fahrenheit). Products with HH in the name maintain integrity up to 90 degrees Celsius (194 degrees Fahrenheit).
What Is TFFN?
TFFN stands for Thermoplastic Flexible Fixture Nylon. In TFFN, the FF represents a flexible fixture. The flexible portion relates to the smaller size of the wire that allows it to move and flex more easily than heavier cables. Fixture means that the applications for this type of wire are electrical fixtures.
THHN Vs. TFFN
THHN and TFFN are different types of wires used for varying applications. These products have many similarities, particularly their thermoplastic nylon construction, which is why they share the letters T and N. However, each has ratings that make it a better choice for certain applications.
Generally, both types work well when you need a thermoplastic nylon option. However, THHN is better for applications that need a greater size range, and TFFN works best in fixtures.
When seen next to each other, the main difference between THHN and TFFN wiring is apparent. The latter comes in much smaller sizes compared to the former. Having more gauge options for THHN means it has more applications for higher power uses than TFFN conductors.
While TFFN has more flexibility, THHN has the advantage of sizing because it ranges from 14 AWG to 1,000 Thousand Circular Mils (MCM). TFFN, however, fits applications where NEC requires fixture wire, while THHN would not.
THHN Vs. THWN
Along with THHN and TFFN, there’s also THWN, which translates to Thermoplastic Heat-Resistant Water-Resistant Nylon-Coated. THWN is similar to THHN, except it is water-resistant, adding the W into the acronym. The W means that it has a rating for use in wet locations. The water resistance of THWN allows it to be installed outdoors and in conduit when the THHN wire cannot.
In addition, this thermoplastic nylon-jacketed wiring can operate up to 75 degrees Celsius. The nylon coating looks like a piece of plastic over a shoelace, protecting the wire in a similar fashion. The THHN wire without dual approval from THWN is not water-resistant. It means you can only install THHN in dry settings.
THHN Vs. THW
While THWN and THW are often used interchangeably due to their water resistance capabilities, they vary in materials used. Instead of a nylon jacket, THW comes with PVC insulation. Without the nylon coating, THW costs slightly less than THHN.
The Revolution of THHN, THWN and THW Wires
Years ago, each wire was made for a specific installation. THHN, THWN and THW are all types of single-conductor electrical wires used in homes and buildings to deliver power. Previously, each acronym was a completely different wire with different approvals. Each type was specific to an application, but now, you’ll typically find their capabilities combined in the THHN/THWN-2 design.
For products named THWN/THHN, the wire is a dual rating type of wire and may also have the label of MWR for machine wire rated on it. That’s why it’s always important to check the wire specifications for the wiring-rated uses in dry or wet locations.
The universal wiring eliminates the challenges associated with the design, manufacturing and availability of each type of electrical wire.
Understanding More About THHN Wires
THHN wire can come in a wide range of configurations, but at the heart of it all, you’ll find several benefits associated with each part of the acronym:
- Thermoplastic: Thermoplastic insulation includes materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene (PE). They are easy to work with and can be stripped if needed. This type of insulation also offers a range of performance characteristics and provides easy identification through different colors.
- High-heat resistance: These wires are rated for up to 194°F or 90℃, providing plenty of room for use in most buildings.
- Nylon coating: The nylon jacket around the wire protects it from abrasion and cuts, as well as various destructive agents like oil, chemicals and water.
To better understand the THHN wire definition, let’s delve into its key attributes. The PE and PVC materials of the THHN cable offer an exterior strip that easily cuts and connects to the wiring. The wires inside the THHN handle high heat temperatures, making them suitable for most applications in buildings.
The copper wire inside the insulation comes in stranded and solid constructions. Solid copper is available in 14, 12 and 10 American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes. All other sizes have stranded copper inside. The nylon jacket that surrounds the internal core and insulation provides protection against wear and tear.
THHN conductor is at the core of underground feeder cable (UFB) and Romex cables. The former does not require a conduit and can run outside or underground. Due to its cost, UFB cable is usually used only in outdoor or buried applications. The more cost-effective Romex cables are a popular choice among contractors for interior electrical wiring in homes and businesses.
What Is THHN Wire Used For?
The THHN wire specifications depend on the application in which they are used. For indoor applications and industries, THHN works for electrical applications needed in:
- Residential buildings
- Commercial buildings
- Locations unexposed to weather
Does THHN Wire Come in Different Colors?
Yes, THHN wire comes in a standard 10 colors, including black, brown, blue, gray, green, orange, red, violet, white and yellow. You might find THHN wire in pink, but it’s less common. You can also stripe THHN if you need another color option. Typically, the green wire is made green with a yellow stripe.
Does Electrical Wire Come Without the Nylon Coating on the Wire?
Yes, you can get something called THW wire, which simply removes the “N” that stands for “nylon.” It can be hard to find THW because there aren’t many manufacturers that stock this wire. One option is to use hook-up wire instead. But keep in mind that it will be much more flexible than electrical wire.
Hook-up wire can come in bare copper instead of the usual tinned copper, and the smaller American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes can come in a solid version. However, the bigger AWG sizes will be much more flexible than the standard electrical wire, so you’ll need to be careful, or it might get bunched into the conduit. If you need a nylon-free wire, you can always reach out to us, and we’ll help you determine the most effective solution.
What’s the Difference Between Romex® and UFB cable?
Romex® and UFB cables are both made with THHN wires on the inside of the cable and provide the exact same function. However, Romex® wire was made to be an indoor cable with a cheap outer jacket to make it more affordable for electrical contractors.
The UFB cable is an underground cable used outdoors because of its tough outer jacket. The “B” in UFB stands for ground wire. Most UFB cables come with a ground wire because it’s usually needed for the job.
What Use Is THHN Wire Suitable For?
When temperatures could exceed 75 degrees Fahrenheit, THHN conductors can stand up to the heat. THN or THWN wiring does not have the same heat resistance.
THHN wiring typically comes in larger sizes than TFFN cable, so it does not have as much flexibility as TFFN products. Common sizes used in Romex or UFB cable of THHN wiring include 10, 12 and 14 AWG. Typically, Romex cable has three of these conductors inside.
Larger sizes of THHN wiring in 8, 6, 4 and 2 AWG are available for applications that need higher voltage, such as supplying a high-voltage outlet for an appliance.
The biggest sizes of THHN wiring are 1/0 and larger. These high-capacity wires can handle circuitry coming from an electrical main to a building. These main supply lines may have smaller THHN or TFFN wires as branch circuits to supply individual outlets or fixtures.
Learning More About TFFN Wires
The “flexible” portion of its name alludes to its ease of movement and flexing. The smaller size of TFFN cables typically accounts for this flexibility. This wire is available only in sizes 16 and 18 AWG, making it much smaller than any available THHN conductors. Inside, the copper wire has a stranded construction.
A rare variation of TFFN cable is the TFN type. This wiring is not as flexible because it contains a solid copper core inside instead of stranded wire. Most applications will require TFFN instead of TFN products.
These wires consist of a bare copper conductor surrounded by PVC insulation and a nylon coating, which gives its flexible characteristics. There is no ground wire and only one conductor in type TFFN wire. Common TFFN wire applications include machine tool wire and appliance wire.
Another bonus to TFFN wire is its array of colors, which allows for easy identification. We carry TFFN wire in black, blue, brown, gray, green, orange, red, violet, white and yellow.
The insulation and coating of TFFN make the cable resistant to threats such as:
- Oil
- Water
- Heat
- Gas
- Moisture
Key Features of TFFN
When used in dry conditions, the wire can handle temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius. Unlike THHN cabling, which you cannot use in wet locations, TFFN cables often allow for safe use in moist places. The downside to using this wiring in wet locations is a drop in its heat resistance.
The use of TFFN conductor in both wet and dry applications comes from its durable exterior, which offers protection against external elements. It also can withstand underground use in a suitable conduit.
TFFN has more flexibility than some other cables, and the National Electric Code (NEC) labels it as fixture wire, which means it can be used in some applications that other cables can’t. It’s also resistant to many common threats that would otherwise lead to fast deterioration. One limitation of TFFN wire is its size — it’s only available in American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes 16 and 18.
What Temperature is TFFN Wire Rated For?
TFFN wire is rated for wet and dry conditions at 600 volts, with temperatures up to 90℃ in dry environments.
You can view a TFFN ampacity chart on each product page.
TFFN vs. TFN
TFFN is closely related to another wire, TFN, which is missing the “F” that stands for “flexible.” Instead of being stranded, TFN uses solid wire, which makes it much stiffer.
We can also supply you with 16 AWG hook-up wire as a more flexible option and 16 AWG polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) wire for a higher-temperature option. The insulation of each type of electrical wire will determine where it can be installed based on the amount of protection it offers.
Approvals and Specifications
TFFN has several approvals and specifications from various organizations:
- Appliance Wire Material (AWM) and Machine Tool Wire (MTW)
- Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH)
- Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
- UL 1063
- UL 66
- UL 758
When you work with a trusted seller like WesBell Electronics, you can rest easy knowing your cables meet the appropriate standards.
How Is TFFN Wiring Used?
A TFFN conductor has many applications due to its smaller size and greater flexibility, which means that wiring rated up to 600 volts is needed. For situations that require fixture wire, use TFFN. Fixture wiring is the main use for TFFN wire.
When using wiring for fixtures, it must remain inside a light fixture or connect the fixture to the branch circuit. The capacity of TFFN wiring to stand up to high heat levels is especially beneficial when used inside lighting fixtures that could have higher operating temperatures than the surrounding environment.
You could use TFFN wiring for control circuits. However, for branch and main circuits, use larger THHN wiring to handle the higher amounts of power.
Which Is Best: TFFN vs. THHN vs. THWN?
If you’re still comparing TFFN vs. THWN or TFFN vs. THHN, consider the following uses for each type of conductor and their main distinctions.
First, THHN and THWN from WesBell Electronics are the same products. They have applications in both wet and dry environments and come in gauges from 14 AWG to greater than 1/0. Due to their larger sizes, THHN and THWN cables do not have the same flexibility that TFFN wiring does. However, these heavier cables have the capacity to carry greater amounts of power, such as main circuits or branch circuits. Romex and UFB cables frequently have three THHN conductors inside for interior or exterior wiring.
TFFN cable only comes in 16 and 18 AWG. The smaller sizes of these cables make them readily flexible for use inside fixtures. They also work well when connecting fixtures or controls to the branch circuits. While capable of handling moisture, the heat resistance of TFFN cables drops in wet environments.
Questions to Ask When Selecting Between THHN and TFFN Wires
You can ask several questions to find the correct wire type to use for your application.
What Temperature Rating Does the Product Need to Withstand?
When used in dry conditions, both THHN and TFFN can handle high heat. However, for wet situations, TFFN’s ability to withstand high temperatures drops. Consequently, if you need protection in a moist environment and high heat resistance up to 90 degrees Celsius, THHN conductors may suffice if other conditions apply.
Where Will You Use the Wiring?
Where you plan to use the wiring also makes a difference. For instance, if you need cables for inside light or appliance fixtures, you must use TFFN, which has a rating for fixtures. THHN is too thick and inflexible for this use. However, smaller TFFN cables do not suffice for large main or branch circuits.
What Gauge Do You Need for the Project?
The gauge needed for the conductor will provide the main determining factor. THHN conductor comes in larger sizes than those available for TFFN, which only comes in 16 and 18 AWG. THHN, though, has a much wider range of options, starting at 14 AWG, which is larger than the biggest TFFN cable. Sizes for THHN range up to 4/0, which has the capacity of carrying 1,000 amps of power.
Do You Need Main or Branch Circuit Wiring?
If you require wiring that will carry more amps, you need THHN cables. Thanks to the larger sizes available, you can use THHN conductors as main or branch circuit wires indoors or outdoors. TFFN conductor does not have a large enough construction to handle the amps required for these applications.
Get in Touch With WesBell Electronics for High-Quality Wires
You must carefully select wiring to meet the construction codes and building requirements of a project. To help you with any electrical work that you have, we offer a supply of wires, cables and services at WesBell Electronics. If you have a design for a project, we can customize the order based on your design upload and specifications through our wire harness assembly and other services.
With more than 30 years of providing wires and cables to businesses, we can fulfill any needs your company has for wires, cables or custom orders. To find out more about our collection of electrical wires, cables and other services, contact us today.