Oct 16, 2024
Lead Wire Comparison (PVC vs XLPE)
When selecting cables for electrical installations, two common options are PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) cables and XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) cables. Each type of cable has distinct properties that make them suitable for different environments and applications. This article delves into the differences between PVC and XLPE cables in terms of insulation, voltage rating, temperature tolerance, thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
1. Insulation Material
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Insulation
PVC is one of the most widely used thermoplastic materials for cable insulation. It is known for its flexibility and versatility in various applications, ranging from household wiring to industrial installations.
- Composition: PVC is a synthetic plastic polymer that becomes soft when heated and hardens upon cooling. This thermoplastic property allows it to be molded into various shapes and structures.
- Performance in Insulation: PVC serves as an effective electrical insulator and is commonly used in low- and medium-voltage applications. Its primary advantage is its cost-effectiveness, as PVC is relatively inexpensive to produce and process.
- Limitations: While PVC is a good insulator for general purposes, it is not ideal for applications requiring high-temperature resistance or where high mechanical strength is needed. When exposed to high temperatures, PVC can degrade and release harmful substances like hydrogen chloride.
XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) Insulation
XLPE, on the other hand, is a thermoset material created by cross-linking polyethylene molecules, resulting in a more stable and durable material.
- Composition: In the production of XLPE cables, polyethylene undergoes a chemical process known as cross-linking. This process transforms the thermoplastic nature of polyethylene into a thermosetting polymer that doesn’t soften or melt under heat.
- Performance in Insulation: The cross-linking significantly enhances XLPE’s thermal and mechanical properties. It provides excellent electrical insulation even at higher voltages, making it ideal for medium- and high-voltage applications. XLPE insulation can also tolerate higher temperatures than PVC without losing its insulating properties.
- Advantages: XLPE insulation is superior to PVC in terms of electrical performance, especially in environments with fluctuating or high temperatures.
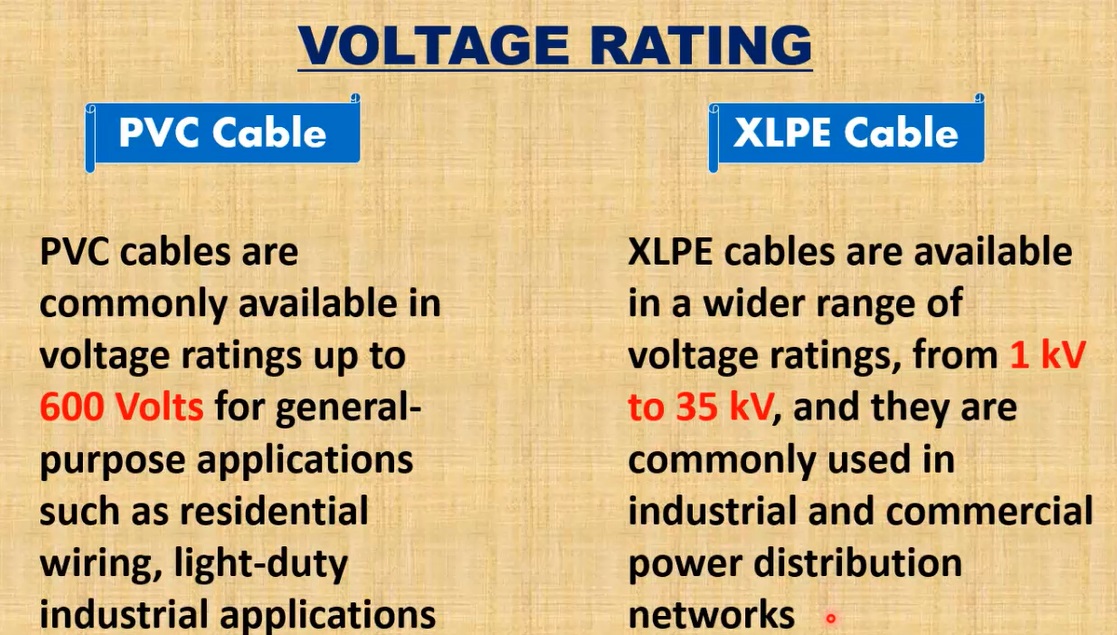
2. Voltage Rating
PVC Cables
PVC-insulated cables are commonly used for low- and medium-voltage applications, typically ranging from 0.6/1kV to 11kV.
- Typical Voltage Applications: These cables are suitable for household wiring, small-scale industrial applications, and machinery that doesn’t require extremely high voltage.
- Insulation Thickness: Due to its lower thermal and dielectric strength, PVC insulation requires a thicker layer to safely carry voltage without breakdown. As a result, PVC cables tend to have a larger outer diameter for the same voltage rating compared to XLPE cables.
XLPE Cables
XLPE-insulated cables are primarily used in medium- to high-voltage applications, ranging from 1kV to 132kV or more.
- High-Voltage Applications: XLPE’s superior insulation capabilities allow it to handle significantly higher voltages. This makes XLPE the go-to choice for power distribution in grids and large-scale industrial operations.
- Efficiency at High Voltages: Because of its excellent dielectric strength, XLPE insulation can be thinner compared to PVC for the same voltage rating. This allows XLPE cables to carry higher voltages with reduced thickness and weight, contributing to more efficient installations in high-voltage environments.
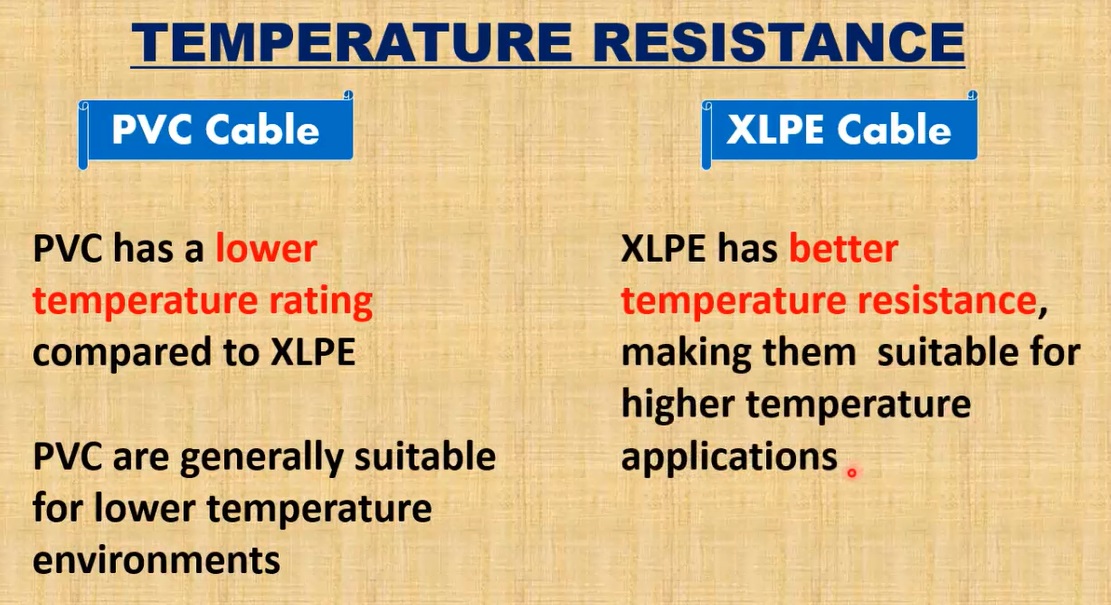
3. Temperature Tolerance
PVC Cables
PVC insulation is limited in its temperature tolerance.
- Operating Temperature Range: Typically, PVC cables can operate in temperatures between -10°C to +70°C. However, specialized PVC formulations can withstand up to +90°C.
- Heat Degradation: Prolonged exposure to temperatures beyond this range can cause the material to soften, lose its structural integrity, and even degrade chemically. As PVC heats up, it tends to release hydrochloric acid, which is corrosive and poses a risk to nearby components.
XLPE Cables
XLPE cables have a much higher tolerance for temperature fluctuations.
- Operating Temperature Range: XLPE cables can generally withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to +90°C during continuous operation. Under emergency conditions, these cables can tolerate temperatures up to +140°C for short durations, and even up to +250°C under specific fault conditions.
- High-Temperature Stability: XLPE’s cross-linked molecular structure allows it to maintain its insulation properties and mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures. This makes it the ideal choice for environments where cables are exposed to high temperatures for extended periods, such as power plants, industrial facilities, and outdoor applications where cables may be subject to direct sunlight.
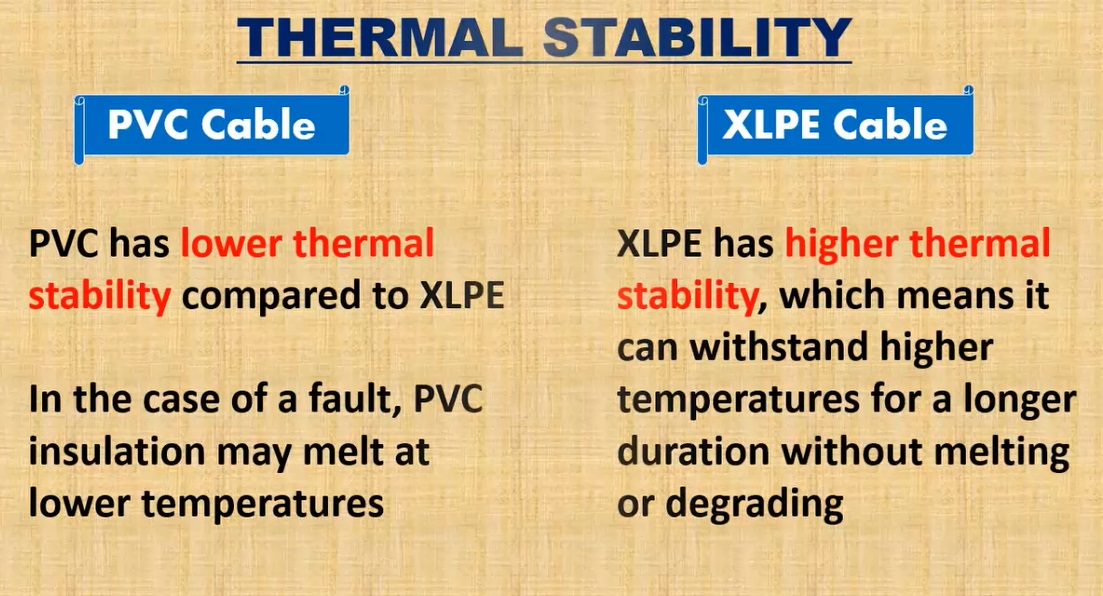
4. Thermal Stability
PVC Cables
PVC’s thermal stability is moderate and may degrade at higher temperatures. This can result in deformation and insulation failure under prolonged exposure to high thermal loads.
- Thermal Expansion: PVC has a higher rate of thermal expansion compared to XLPE, meaning it is more likely to expand or contract with changes in temperature. This can lead to mechanical stress on the cable joints and terminations, making it less suitable for environments with wide temperature fluctuations.
- Aging and Degradation: Over time, the plasticizers used in PVC can break down, especially when exposed to heat, leading to the hardening and cracking of the insulation. This process is accelerated in environments where cables are exposed to direct sunlight, UV radiation, or high temperatures.
XLPE Cables
XLPE offers superior thermal stability, allowing the cables to maintain their shape and structural integrity even under high-temperature conditions.
- Low Thermal Expansion: The cross-linked structure of XLPE provides excellent resistance to thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring that the insulation remains stable under varying temperature conditions. This property makes XLPE cables particularly suitable for high-stress environments like power stations and outdoor installations.
- Longer Lifespan: XLPE cables are less prone to aging and insulation degradation compared to PVC cables, which is why they are often the preferred choice in long-term installations.
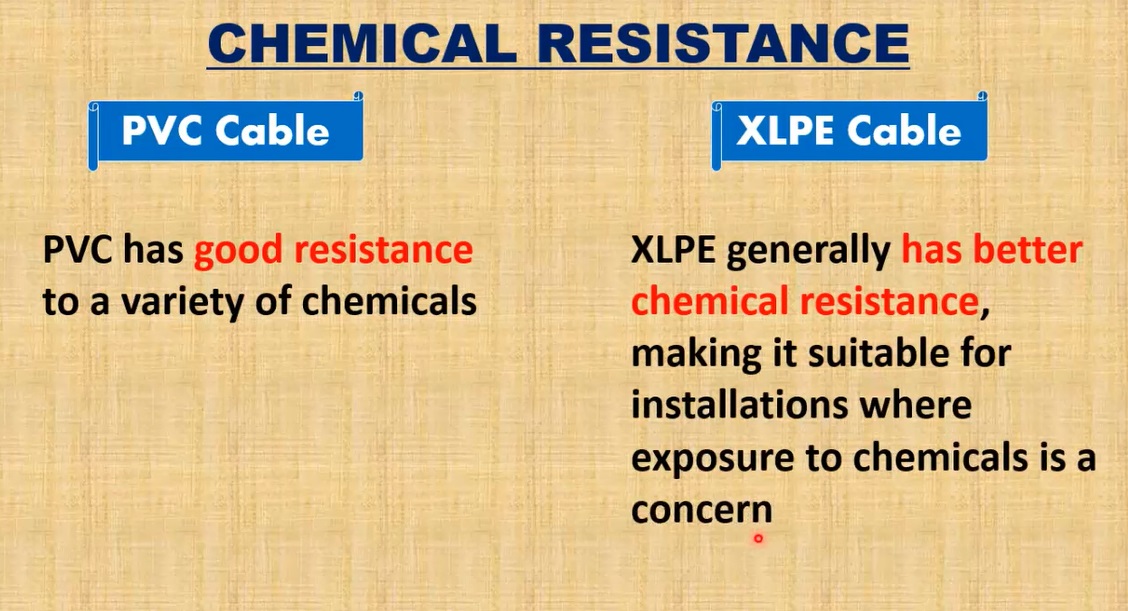
5. Chemical Resistance
PVC Cables
PVC cables offer good resistance to certain chemicals but have some limitations.
- Resistance to Acids and Alkalis: PVC is generally resistant to a wide range of acids and alkalis, making it a good choice for indoor installations where chemical exposure is limited.
- Vulnerability: However, PVC is not as resistant to oils, solvents, or greases. Prolonged exposure to these substances can cause PVC to degrade, leading to insulation failure.
- Corrosive By-Products: One significant drawback of PVC is that when it burns or degrades under high temperatures, it releases corrosive hydrogen chloride gas. This gas can cause damage to nearby equipment, particularly in confined spaces like control rooms or switchgear enclosures.
XLPE Cables
XLPE cables have superior chemical resistance compared to PVC cables.
- Chemical Stability: XLPE is highly resistant to most oils, solvents, and chemicals, making it an excellent choice for industrial environments where exposure to hazardous substances is more likely.
- No Corrosive Emissions: Unlike PVC, XLPE does not release corrosive by-products when exposed to heat or fire, making it a safer option in environments where fire safety is a concern.
6. Mechanical Strength
PVC Cables
PVC cables offer moderate mechanical strength and flexibility.
- Tensile Strength and Flexibility: PVC cables are flexible and easy to work with, making them ideal for installations where cables need to be routed through tight spaces or bent around corners. However, this flexibility comes at the cost of mechanical strength, as PVC can be susceptible to mechanical damage under impact or pressure.
- Durability: PVC cables are more prone to abrasion, cuts, and physical damage, especially in outdoor environments or installations with heavy machinery. Over time, mechanical stress can lead to cracks in the insulation, increasing the risk of short circuits or insulation failure.
XLPE Cables
XLPE cables have significantly better mechanical strength and durability.
- High Tensile Strength: The cross-linked molecular structure of XLPE gives it excellent tensile strength, making it resistant to stretching, impact, and mechanical damage.
- Abrasion Resistance: XLPE cables are highly resistant to wear and tear, making them suitable for outdoor installations or environments where cables may be exposed to heavy machinery or foot traffic.
- Flexibility: While XLPE cables are generally less flexible than PVC cables, they are still suitable for most installations where mechanical strength and durability are prioritized over flexibility.
7. Fire Resistance and Safety
PVC Cables
PVC is a flame-retardant material, which means it can self-extinguish when the source of the fire is removed. This makes it suitable for general electrical wiring in buildings. However, its fire resistance has limitations.
- Toxic Emissions: When PVC burns, it releases harmful gases such as hydrogen chloride (HCl) and dioxins. These gases can be highly toxic and corrosive, posing risks to both human health and equipment. In confined spaces, this can be a significant safety concern, especially in cases of fire.
- Flame Propagation: PVC cables can contribute to flame propagation in some cases, although flame-retardant additives are commonly used to improve their performance in fire scenarios.
XLPE Cables
XLPE is not naturally flame-retardant, but its superior insulation properties allow it to withstand high temperatures for longer durations.
- Low Smoke and Zero Halogen (LSZH): XLPE cables can be manufactured with low smoke and zero halogen properties, making them much safer in fire scenarios. These cables do not emit toxic or corrosive gases when exposed to fire, reducing the risk to both humans and equipment in case of a fire.
- Fire Safety in Critical Installations: Due to their low smoke and halogen-free nature, XLPE cables are often used in critical applications where fire safety is a top concern, such as in public buildings, underground railways, and data centers.
Conclusion
When comparing PVC and XLPE cables, each has its distinct advantages and applications:
- PVC cables are more affordable, flexible, and widely used in low- and medium-voltage applications where high temperatures or chemical resistance are not primary concerns.
- XLPE cables offer superior insulation, higher voltage ratings, excellent temperature tolerance, greater thermal stability, better chemical resistance, and stronger mechanical properties, making them ideal for high-voltage, industrial, and outdoor environments.
The choice between PVC and XLPE cables ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the installation, such as voltage rating, environmental conditions, and mechanical stresses. In demanding environments that require high performance in terms of thermal and chemical resistance, XLPE cables outperform PVC. However, for general-purpose installations, PVC remains a cost-effective and reliable option.