Sep 24, 2024
Ways of Cutting, Coiling, and Stripping Multiconductor Portable Cables
1. Cutting Multiconductor Portable Cables
Multiconductor portable cables are often used in industrial applications because they are flexible and can endure harsh environments. These cables consist of multiple insulated conductors within a protective jacket, often made from rubber or another durable, flexible material. Cutting and coiling these cables requires careful attention to detail to avoid damaging the conductors or insulation.
Tools Required:
- Cable cutters or shears
- Utility knife or cable stripping tool
- Measuring tape
- Cable clamp or holder (for keeping the cable stable)
Steps to Cut the Cable:
- Step 1: Measure and Mark: Begin by measuring the required length of cable with a measuring tape. Use a marker or tape to mark the location where the cable will be cut.
- Step 2: Secure the Cable: To prevent any movement while cutting, clamp the cable to a stable surface or hold it firmly. This reduces the risk of jagged edges and potential conductor damage.
- Step 3: Use Appropriate Cable Cutters: Depending on the cable’s size, a sharp set of cable cutters should be used. Portable multiconductor cables are typically thick due to their jacket and multiple insulated conductors, so using the correct cutters is essential. The cut should be clean and smooth to avoid fraying or damaging the internal components.
- Step 4: Trim Any Frayed Wires: If there is any fraying of the individual conductors after cutting, use small wire cutters to trim them to even lengths.
2. Coiling SOOW Cable
Proper coiling of the cable helps prevent kinks, tangles, and premature wear, especially when storing or transporting cables.
Steps for Coiling:
- Step 1: Find the Natural Coil Pattern: Most cables will naturally want to coil in a specific direction. Let the cable guide you, and avoid forcing it into tight bends. This prevents strain on the internal conductors.
- Step 2: Lay the Cable Flat: Lay the cable flat on a smooth surface, ensuring it is free from any kinks or tangles.
- Step 3: Begin Coiling: Start by loosely forming large loops, approximately 1 to 2 feet in diameter, depending on the cable’s thickness. Over-tightening the loops can create stress points where the cable could crack or lose its structural integrity.
- Step 4: Secure the Coiled Cable: Use cable ties, Velcro straps, or bungee cords to keep the coils secure. Ensure the loops are not too tight, as you want to avoid putting excess pressure on the cable jacket.
3. Removing the Rubber Jacket of SJOOW Cable
When working with multiconductor portable cables, removing the outer jacket must be done carefully to avoid cutting into the conductor insulation. The jacket is typically made of rubber, neoprene, or a similar material to provide flexibility and environmental protection.
Steps to Remove the Jacket:
- Step 1: Mark the Jacket: Measure the length of jacket you need to remove. This is typically enough to expose the conductors for termination. Mark this point with a piece of tape or a marker.
- Step 2: Score the Jacket: Using a utility knife or cable stripping tool, lightly score the surface of the rubber jacket along the marked line. Be very careful not to apply too much pressure, as cutting too deep can nick the insulation on the individual conductors beneath.
- Step 3: Peel Back the Jacket: After scoring, gently bend the cable to cause the scored section to split. Peel the jacket back by hand. If necessary, use pliers to pull the jacket away. Avoid using excessive force to prevent damage to the conductors inside.
- Step 4: Trim the Jacket: Once the jacket is peeled back, cut it off cleanly with your utility knife or shears.
4. Semi-Stripping Conductor Insulation
Semi-stripping refers to the process of partially removing insulation from the conductor to prepare it for crimping or other terminations. This method helps ensure proper connectivity while avoiding damage to the conductor.
Steps to Semi-Strip Insulation:
- Step 1: Measure the Strip Length: Measure how much insulation needs to be removed based on the terminal or connector being used. Mark the insulation with a marker or tape.
- Step 2: Use a Wire Stripper: Select the correct size on your wire stripping tool to match the conductor’s gauge. Align the marked spot with the tool’s blade.
- Step 3: Cut the Insulation: Apply gentle pressure to the tool to cut through the insulation without nicking the wire strands underneath. The goal is to score the insulation and not the conductor itself.
- Step 4: Slide the Insulation Off: Gently pull the insulation off, leaving the exposed conductor intact. In semi-stripping, you may leave a small portion of the insulation attached to ensure it doesn’t accidentally get pulled off during handling.
Upgrading Power Cables: Type W, Type G, and Type G-GC
Upgrading to advanced types of portable power cables can provide substantial benefits, particularly in industrial or heavy-duty environments. Each cable type—Type W, Type G, and Type G-GC—has specific design improvements that enhance safety, performance, and durability.
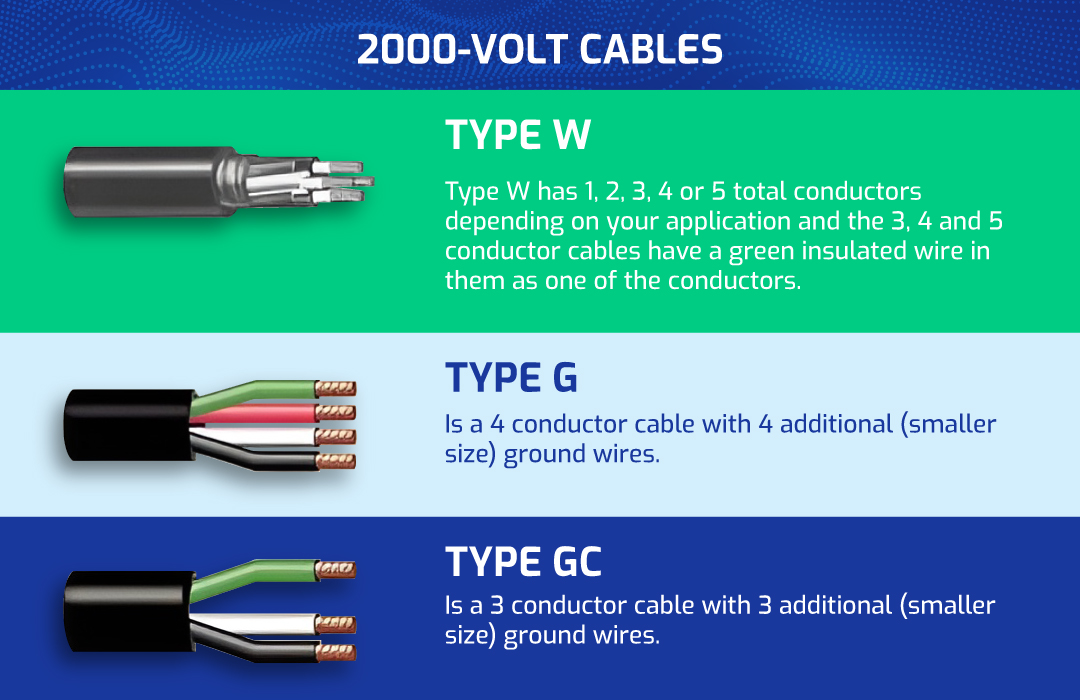
1. Type W Cable
Type W cables are designed for heavy-duty power distribution in demanding environments, such as mining, construction, and entertainment. They are known for their robustness, high flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear.
Construction:
- Conductor: Type W cables use finely stranded copper conductors, which provide excellent conductivity and flexibility.
- Insulation: The conductors are insulated with ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR) or similar materials, providing good resistance to heat, moisture, and chemicals.
- Jacket: The outer jacket is typically made of thermoset rubber (like chlorinated polyethylene), which is durable and resistant to oil, sunlight, and abrasion.
Applications:
- Used in temporary power systems for industrial, mining, and construction sites.
- Suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments.
- Can withstand exposure to extreme temperatures, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
Benefits of Upgrading to Type W:
- Enhanced Durability: Type W cables are highly resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation.
- Flexibility: Even with thick insulation, Type W cables remain flexible, making them easier to handle and install in tight spaces.
- Long Life: Due to their durability, they offer a longer service life compared to standard power cables, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
2. Type G Cable
Type G cables are also heavy-duty power cables but are specifically designed to carry multiple ground wires, making them ideal for applications requiring additional grounding.
Construction:
- Conductor: Made from stranded copper for good flexibility and electrical performance.
- Insulation: Typically insulated with EPR, providing high dielectric strength and resistance to moisture and heat.
- Jacket: The outer jacket is typically made from chlorinated polyethylene (CPE) or other durable materials, ensuring resistance to oil, weather, and mechanical damage.
Unique Feature: Type G cables come with four ground conductors, which provide enhanced grounding capabilities, crucial for environments where additional safety measures are required.
Applications:
- Ideal for mining, drilling, or other applications where equipment may experience high levels of mechanical stress.
- Used in situations where extra grounding is required for safety, such as in explosive or hazardous environments.
Benefits of Upgrading to Type G:
- Improved Grounding: With multiple ground wires, Type G cables provide superior grounding performance, which is crucial for safety in high-power industrial environments.
- Safety: The enhanced grounding system minimizes the risk of electrical shock, making them ideal for hazardous environments.
- High Voltage Rating: Type G cables can carry higher voltages (up to 2000V) compared to standard portable cables.
3. Type G-GC Cable
Type G-GC (Ground-Ground Check) cables are a further evolution of Type G cables, incorporating an additional ground check conductor for even more robust safety features.
Construction:
- Conductor: Stranded copper, ensuring flexibility and conductivity.
- Insulation: Like Type G, Type G-GC cables typically use EPR for insulation, providing resistance to high temperatures, moisture, and mechanical wear.
- Jacket: The jacket is usually made from CPE or a similar material that is resistant to oil, sunlight, and abrasions.
Unique Feature: In addition to the multiple ground wires found in Type G cables, Type G-GC cables include a ground check conductor, which is used in systems to monitor the integrity of the grounding system. This is crucial for maintaining a continuous ground connection in situations where the ground may become compromised.
Applications:
- Used in mining operations, heavy industrial applications, and construction where safety and grounding continuity are of paramount importance.
- Ideal for high-vibration environments where grounding may be disrupted.
Benefits of Upgrading to Type G-GC:
- Enhanced Safety Monitoring: The ground check conductor allows for continuous monitoring of the ground system, reducing the risk of electrical failure.
- Durability: Like Type G, Type G-GC cables are highly resistant to environmental factors such as oil, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Flexibility and Ease of Use: Despite their heavy-duty construction, these cables are flexible enough for easy installation and handling in complex environments.
Conclusion
Working with multiconductor portable cables requires precision and care, especially when cutting, coiling, and stripping the jacket and insulation. Proper techniques help ensure the integrity of the conductors and their insulation, preventing damage that could lead to electrical hazards. Additionally, upgrading power cables to more advanced types like Type W, Type G, or Type G-GC can significantly improve safety, durability, and performance in industrial settings. These cables are designed to withstand extreme conditions while providing enhanced electrical properties and safety features such as improved grounding and resistance to environmental factors. As industrial power needs grow, investing in upgraded cables can provide long-term benefits in safety, performance, and cost-efficiency.